Flash memory programming of the Nuvoton microcontrollers
Background
The modern microcontrollers utilize the flash memory instead of EEPROM as the code memory, achieve code memory programming without a stand alone programmer. This artical will present the principle and the multiple way to programming with code memory by the Nuvoton’s chips, also please note that, different brands may have different definitions of the technical terms used below.
Basic knowledge
In-Circuit Emulation (ICE)
ICE enabled processor core registers and memory access through the external debug probe such like Nu-Link, ST-LINK, J-Link or something else. It helps developer to track the execution status of the microcontroller without braking the functionality of the target circuit. The common interface of the ICE is Serial Wire Debug Port (SW-DP or SWD) and JTAG-DP which spec in the ARM Debug Interface Architecture Specification. Nuvoton’s chips usually provide the SWD as the ICE interface.
Flash Memory Controller (FMC)
FMC is a interface between system memory and on-chip flash memory, it allow us to access flash memory via FMC registers which is already located in System Memory Map.
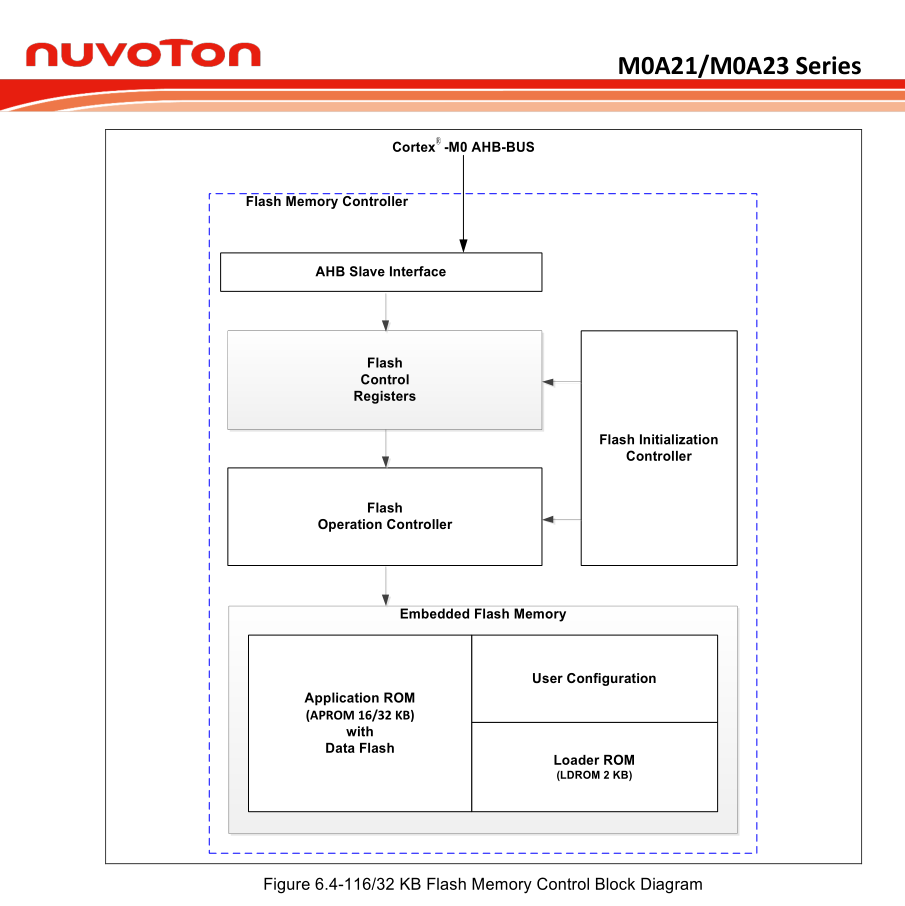
Flash memory organization
Most of the Nuvoton’s chips has three different sections of flash memory, inclueds APROM, LDROM, and Data Flash. In generaly, APROM is used to store the program which provide to the target application, LDROM is used to store the bootloader which will execute before the application. The Data Flash is shared with APROM, it determin by DFBA in config bits which can be program by user, and it can be program through ISP Commands without unlocking the write permission of APROM.
Chip Booting Selection (CBS)
The CBS in the config bits determin the booting mode for the chip, there are four booting mode includes LDROM with IAP, LDROM without IAP, APROM with IAP, and APROM without IAP. If the chip boot without IAP mode, APROM and LDROM will only have one of them present in the System Memory Map, which means can only access them self while CPU executing the code in it.
Memory map
In most of the Nuvoton’s chips, the Flash Memory Map is different from System Memory Map. The Flash Memory Map is used for the FMC to access flash memory. And the System Memory Map is what CPU looking through. The flash memory can be map into the System Memory Map, the map address is setup by Chip Booting Selection (CBS) in the config bits. For example, the Flash Memory Map of LDROM start at 0x00100000 it can be map to 0x00000000 in the System Memory Map by select Boot from LDROM without IAP mode in CBS.
| Booting mode | CBS | APROM mapping address | LDROM mapping address | Data flash mapping address | Vector table |
| LDROM with IAP | 00 | 0x00000000 | 0x00100000 | DFBA | Remap to LDROM |
| LDROM without IAP | 01 | 0x00000000 | 0x00000000 | DFBA | Depends on executing location |
| APROM with IAP | 00 | 0x00000000 | 0x00100000 | DFBA | Remap to APROM |
| APROM without IAP | 01 | 0x00000000 | 0x00000000 | DFBA | Depends on executing location |
In-System Programming (ISP)
FMC provide ISP Commands include read, erase, program, and vector remap. Accessing the FMC registers with corresponding commands and data via firmware or ICE can produce the flash memory programing. If you are doing APROM update by the firmware, it has a separate firmware usually called bootloader which located in LDROM to interact between FMC and the others peripheral such like UART, USB, CAN.
In-Circuit Programming (ICP)
ICP utilize the memory access feature of ICE, sending the ISP Commands direct to the FMC registers without firmware. It needs a programming tool (software) to handle the commands and data between host computer, debug probe and FMC registers. Nuvoton provide NuMicro ICP Programming Tool which can be download from their website. If you are using a brand-new chip, it’s supposed to to use the ICP to program your code, either APROM or LDORM.
In-Application Programming (IAP)
IAP brings more flexibility to the developers. If the IAP function is enabled by the CBS[0], the whole flash memory will appear in System Memory Map. This means CPU can executing the code in APROM, LDROM even the SRAM without rebooting the chip. IAP mode also let the APROM, LDROM even the SRAM able to map into a 512-byte of Vector Map Space. The Vector Map Space used for the Cortex-M Vector table which contains the reset value of the main stack pointer, the start addresse, and interrupt vector table. IAP brings more flexibility to the developers to customize the code executing location and the interrupt service routine.